Chapter 3 HS Definition and Some Data
Definition:
Homeschooling refers to the practice where parents educate their children at home instead of sending them to public or private schools. Based on my personal experience over the past 10 years, it is ultimately a lifestyle choice.
📊 Homeschooling Statistics in the U.S.
Student Data:
- 1999: The National Center for Education Statistics (NCES) reported approximately 850,000 homeschooled students, accounting for 1.7% of all K–12 students.
- 2003: The number increased to 1.1 million, representing 2% of K–12 students.
- 2007: Approximately 1.5 million students were homeschooled, making up 2.9% of the K–12 population.Wikipedia+3National Center for Education Statistics+3National Center for Education Statistics+3
- 2012: The figure rose to 1.77 million students, or 3.4% of K–12 students.
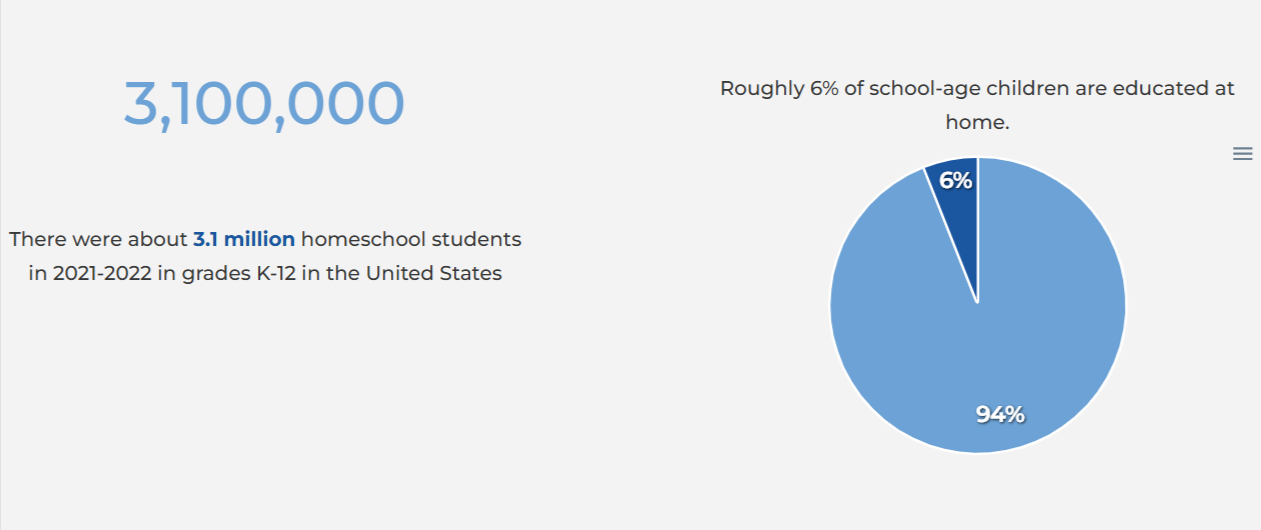
- 2019: An estimated 2.5 million students were homeschooled, about 2.8% of the K–12 population.
- 2020–2021: Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, homeschooling saw a significant increase. The U.S. Census Bureau reported that in the fall of 2020, 11.1% of households with school-age children were homeschooling, up from 5.4% in the spring. Census.gov
- 2022–2023: The NCES reported that 5.2% of children ages 5 to 17 received academic instruction at home during the 2022–23 school year. National Center for Education Statistics+1Coalition for Responsible Home Education+1
The latest statistics of homeschooling can be accessed here.
Parental Education Levels:
According to the NCES, parents without higher education degrees can and do successfully homeschool their children. The distribution of homeschooling across various parental education levels indicates that a college degree is not a prerequisite for effective homeschooling.
📈 Trends and Demographics
Homeschooling has become more diverse over time. Data indicates an increase in homeschooling among Hispanic and African American families. For instance, in 2020–2021, 5.4% of children were reported as homeschooled, with higher percentages among White adults (7.4%) compared to Black adults (5.1%) and Asian adults (3.6%).